
COMPOSITE REPAIR
COMPOSITE REPAIR FOR PIPE AND TANK LEAKS:
COMPOSITE REPAIR
COMPOSITE REPAIR FOR PIPE AND TANK LEAKS:
- Customized solution for through wall defects for pipes and tank walls
- Compliant installed by trained and certified applicators
- Engineering Calculation Report and Method of Statement for each repair
- ISO24817 and ASME PCC2 standards
- Provide excellent strength, bonding and chemical resistance
- Warranty for 20 years


COMPOSITE REPAIR FOR PIPELINE REINFORCEMENT:
- Customized solution for thin wall defects for pipes and tank walls
- Compliant installed by trained and certified applicators
- Suitable for wall loss up to 80%
- Engineering Calculation Report and Method of Statement for each repair
- ISO24817 and ASME PCC2 standards
- Provide excellent strength, corrosion and chemical resistance
- Warranty for 20 years

Introduction
The use of composite materials for the repair of carbon steel pipework has been originally designed in accordance with ASME/ANSI B31.3: Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping. The use of composite materials for the repair of pipework covers the following circumstance
- external corrosion only (no leakage and structural integrity needs to be restored). In this case it is probable that with suitable surface preparation the application of a composite overwrap will arrest further deterioration;
- external damage such as dents, gouges, fretting (at pipe supports) where structural integrity needs to be restored;
- internal metal loss through corrosion or erosion (or a combination of corrosion and erosion), which may or may not be leaking, and there is a need to restore structural integrity. In this case it is probable that internal metal loss will continue and the assessment of the damage and the composite repair option must take this into account
The repaired service lifespan of pipeline can be considered between temporary (up to 2 years) and permanent (remaining lifetime of the piping system).The following repair of composite is also considered capable of operating in excess of 200oC andfor operating pressures up to 50 bar (after post curing application).
Types of Composite Repair System
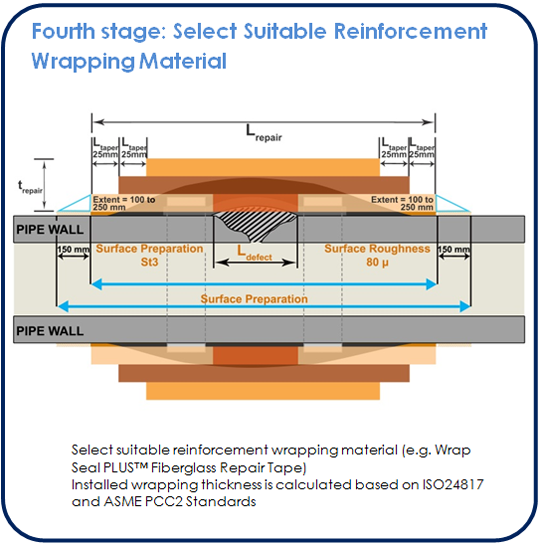
The types of composite repair system fall into 2 generic types: ‘bandage repair kit’ and ‘engineered’. The ‘Bandage repair kit’ type repair of composite (i.e. Wrap Seal leak repair kit) involve the application of pre-packed material, which can be held as a stock repair item and can be applied by maintenance personnel on the facility. The ‘Engineered’ (i.e. Wrap Seal PLUS composite repair system) type of composite repairs are specified and designed on a bespoke basis with the repair being carried out by specialist contractors.
All of the composite repairs involve the application of an overwrap to the damaged or defective area(s) in order to reinforce the strength/integrity of the remaining pipe wall. This may involve the ‘on-site’ production of a composite laminate –a combination of a network of fibrous reinforcement and a thermosetting polymer matrix that is subsequently subject to a chemical curing process –or the use of a pre-formed composite sleeve that is wrapped around the pipe and adhesively bonded to the pipe and to subsequent wraps. In situation where external metal loss is being repaired, repair applications that use a pre-formed composite sleeve must also involve the application of some form of load transferring filler (e.g. SealXpert metal repair putty) to the damaged area prior to application of the composite sleeve (e.g. Wrap Seal PLUS fiberglass repair tape) that is the main design issue.
It has been assumed that the contribution of the steel to the load carrying capability of the repaired section may be ignored.In order to assess the contribution of the damaged steel pipe to the integrity of a repair ASME PCC2 or ISO 24817 standards may be used. This document provides calculation methods for the assessment of the remaining load carrying capability of pipe that has been subjected to corrosion (general and localised, including pitting), mechanical flaws (induced during fabrication or through abuse) and fire. Where the deterioration will continue after repair (e.g. internal corrosion) the document takes this into account through measured corrosion rates. The result of the calculations is a maximum safe or allowable operating pressure (MAOP) for the damaged pipe.
The design approach used in the assessment of the repair must take into account all of the applied loads and the ability of the overwrap to carry these satisfactorily. In some of the repair systems the reinforcement is preferentially orientated circumferentially and in these circumstances will only have limited load carrying capabilities in the axial direction. For complex pipe systems where axial stresses can be significant and where there is sufficient parent metal to carry these loads, the alternative repair options that have similar hoop and axial strengths will need to be considered.
Composite Repair on Leaking Pipes
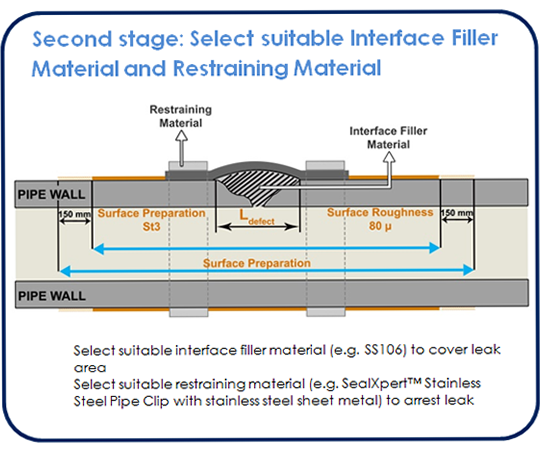
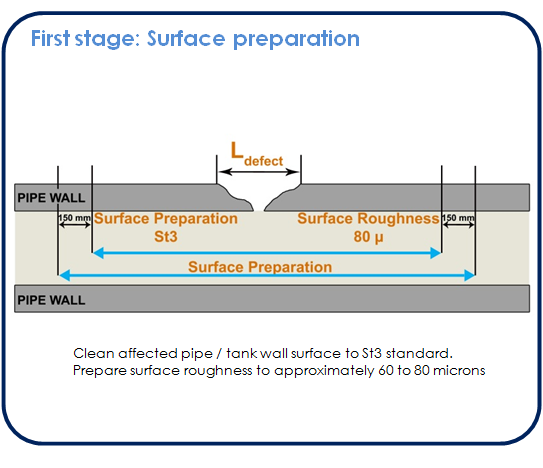
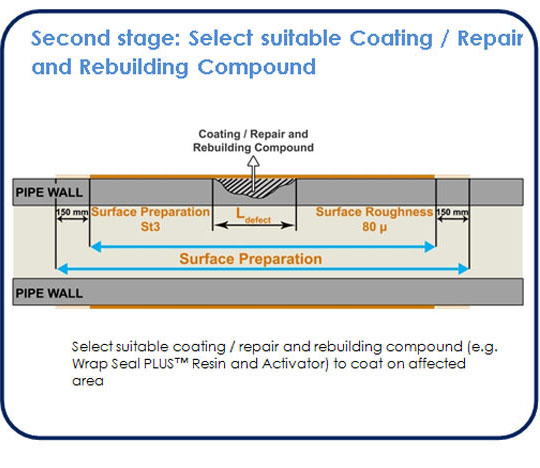
Where the pipe to be repaired is leaking, the effect of this on the likely success of the repair needs to be considered. Whilst the mechanical design of the overwrap is important in determining the success of the repair, by far the single most important issue is that of surface preparation of the parent steel. The next important step is to ensure that the restraining material (e.g. SealXpert stainless steel pipe clip) has effectively stemmed and secured the pipe leak. Only when the leak has been successfully stemmed and secured, subsequent the application of rebuilding material (e.g. SealXpert repair putty) to increase the mechanical strength and laminate wrapping should be carried out.
Whilst there are resin systems for which it is possible to achieve an acceptable bonded connection when surfaces are wet (i.e. when using SealXpert PS106 Underwater Repair Putty), a dry situation is preferred. Isolation and draining of the pipework can provide a dry external surface adjacent to the perforation. Consideration must be given to the compatibility of the composite repair material and the pipework service (transported fluids).
Cure Condition of Repair Laminate
The cure of a repair laminate is strongly influenced by temperature and the correct mixing of the resin constituents prior to lamination. It is important, therefore, that the prevailing temperature conditions are considered. Application outside the temperature limits and resin catalyst levels must not be carried out information.
Documentation & Data Requirements
In order for a composite material supplier to correctly specify a proposed repair option, the operator should provide the following information:
- Pipe Data
- Size & location of pipe defect
- Operating pressure& temperature;
- Pipe medium;
- Required lifetime of the repair.
